How Can I Find the Right Cloud Computing Resources for My Business?
Overview of Cloud Computing Resources
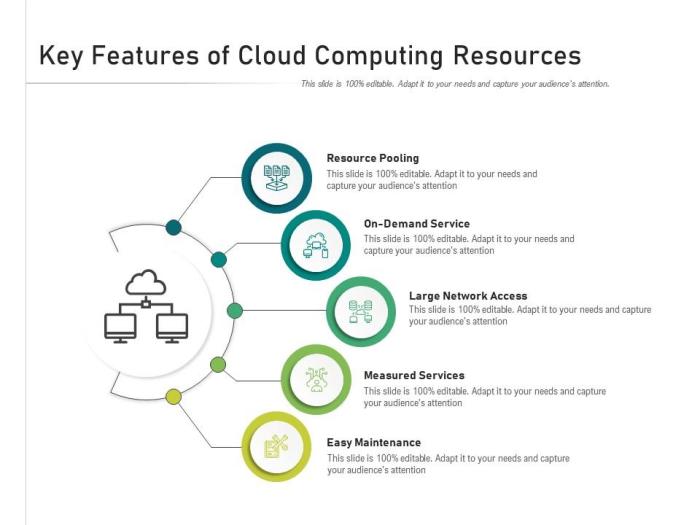
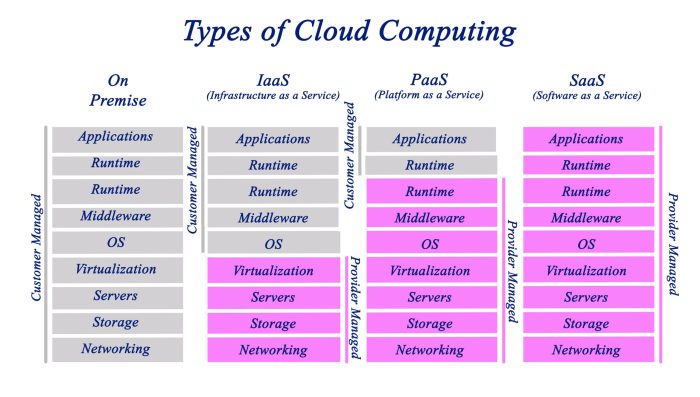
Cloud computing resources encompass a wide range of services and technologies that organizations can leverage to meet their computing needs. These resources can be broadly categorized into three main types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
IaaS provides fundamental computing resources such as storage, networking, and servers. PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. SaaS delivers fully functional applications that users can access through a web browser or mobile device.
Benefits of Cloud Computing Resources
- Cost Savings: Cloud computing eliminates the need for organizations to invest in and maintain their own hardware and software, leading to significant cost savings.
- Scalability: Cloud resources can be easily scaled up or down to accommodate changing business demands, ensuring organizations can adapt quickly to fluctuations in demand.
- Reliability: Cloud providers offer high levels of reliability and uptime, ensuring that applications and data are always accessible.
- Flexibility: Cloud computing provides organizations with the flexibility to choose the services and resources that best suit their specific needs.
Limitations of Cloud Computing Resources
- Security Concerns: Migrating data and applications to the cloud raises security concerns, as organizations need to ensure that their data is protected from unauthorized access.
- Vendor Lock-in: Organizations that rely heavily on a single cloud provider may experience vendor lock-in, making it difficult to switch providers.
- Performance Issues: In certain scenarios, cloud resources may not provide the same level of performance as on-premises infrastructure.
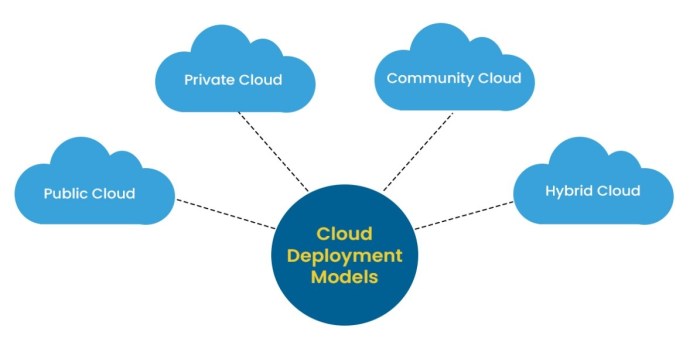
Deployment Models in Cloud Computing
Organizations can choose from various deployment models when adopting cloud computing, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Public Cloud: In a public cloud model, resources are shared among multiple tenants, offering cost-effectiveness and scalability.
- Private Cloud: A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, providing greater control and security but at a higher cost.
- Hybrid Cloud: A hybrid cloud combines elements of both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both models.
- Multi-Cloud: A multi-cloud strategy involves using multiple cloud providers, enabling organizations to distribute their workloads across different platforms.
Key Concepts in Cloud Computing
Several key concepts are essential for understanding cloud computing:
- Elasticity: Cloud resources can be scaled up or down quickly and easily to meet changing demands.
- Scalability: Cloud resources can be scaled horizontally or vertically to accommodate increased workloads.
- Fault Tolerance: Cloud providers implement measures to ensure that applications and data remain available even in the event of hardware or software failures.
Identifying Business Requirements
Understanding business requirements is paramount when selecting cloud computing resources. It ensures that the chosen resources align seamlessly with the organization’s objectives and address its specific needs. A comprehensive analysis of business requirements lays the foundation for making informed decisions and optimizing resource utilization.To
effectively gather and analyze business requirements, follow these steps:
Stakeholder Interviews:
Conduct in-depth interviews with key stakeholders across various departments, including IT, finance, marketing, and operations. Engage in open-ended discussions to grasp their perspectives, challenges, and expectations regarding cloud computing.
Surveys and Questionnaires:
Distribute surveys or questionnaires to a broader employee base to collect quantitative data on their needs, preferences, and pain points. This feedback helps identify common themes and trends that may not emerge from stakeholder interviews alone.
Data Analysis:
Analyze historical data, such as IT infrastructure usage patterns, application performance metrics, and customer feedback, to identify areas for improvement and opportunities for optimization. Data-driven insights complement qualitative feedback from stakeholders and surveys.
IT Strategy and Business Objectives:
Align the cloud resource selection process with the organization’s IT strategy and broader business objectives. Consider how cloud computing can contribute to achieving strategic goals, enhancing operational efficiency, and driving innovation.
Evaluating Cloud Providers
Selecting the right cloud provider is a critical decision that can significantly impact the success of your cloud initiatives. To make an informed choice, it’s essential to evaluate the leading cloud providers based on key criteria and consider factors specific to your business needs.
Below is a table comparing the top cloud providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, etc.) based on key criteria:
| Criteria | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud | Alibaba Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | Pay-as-you-go pricing model with various pricing options and discounts | Pay-as-you-go pricing model with flexible spending options and reserved instances | Pay-as-you-go pricing model with flexible pricing tiers and volume discounts | Pay-as-you-go pricing model with cost-effective options and discounts for long-term usage |
| Features | Wide range of cloud services, including compute, storage, networking, analytics, and AI/ML | Comprehensive suite of cloud services, including compute, storage, networking, databases, and AI/ML | Robust cloud platform with compute, storage, networking, big data, and AI/ML services | Extensive cloud services, including compute, storage, networking, security, and AI/ML |
| Reliability | Highly reliable infrastructure with multiple data centers and redundant systems | Reliable cloud platform with a global network of data centers and high uptime | Reliable and scalable cloud infrastructure with a global presence and multiple data centers | Reliable cloud platform with a global network of data centers and advanced security measures |
| Security | Robust security features, including encryption, access control, and compliance certifications | Comprehensive security features, including encryption, identity management, and compliance certifications | Advanced security features, including encryption, threat detection, and compliance certifications | Robust security features, including encryption, access control, and compliance certifications |
| Customer Support | 24/7 customer support with multiple channels, including phone, email, and chat | 24/7 customer support with various channels, including phone, email, and online forums | 24/7 customer support with multiple channels, including phone, email, and online documentation | 24/7 customer support with multiple channels, including phone, email, and online resources |
When choosing a cloud provider, consider factors such as cost, compliance requirements, industry-specific needs, and the availability of required services. It’s also important to conduct thorough research, read reviews, and seek expert advice to make an informed decision.
Matching Resources to Requirements
Matching cloud computing resources to business requirements is crucial for an effective and efficient cloud adoption. It involves understanding the business needs, assessing resource requirements, and selecting cloud services that align with those requirements.The process of matching resources to requirements typically includes the following steps:
Assessing Resource Needs
- Identify the specific business objectives and requirements that the cloud solution is intended to address.
- Evaluate the current IT infrastructure and applications to determine the existing resource utilization and performance metrics.
- Forecast future growth and scalability needs based on business projections and anticipated usage patterns.
- Analyze the data storage requirements, including the amount of data, type of data (structured, unstructured, etc.), and data access patterns.
- Assess the compute requirements, considering the processing power, memory, and storage capacity needed to run applications and handle workloads.
- Evaluate the networking requirements, including bandwidth, latency, and security considerations for data transmission and communication.
- Identify the security requirements, such as data encryption, access control, and compliance regulations that need to be met.
Selecting Cloud Services
- Research and compare different cloud providers and their service offerings to identify the ones that best match the specific resource requirements.
- Evaluate the performance and scalability capabilities of the cloud services to ensure they can handle the anticipated workloads and growth.
- Consider the cost-effectiveness of the cloud services, including pricing models, usage-based billing, and potential cost savings.
- Assess the reliability, uptime, and disaster recovery capabilities of the cloud services to ensure business continuity and data protection.
- Review the security features and compliance certifications offered by the cloud providers to ensure they meet the security and regulatory requirements.
Optimizing Resource Allocation
- Continuously monitor resource utilization and performance metrics to identify areas where resources can be optimized or reallocated.
- Implement auto-scaling and load balancing mechanisms to adjust resource allocation based on demand, improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Utilize cloud-native tools and services for resource management and optimization, such as cloud cost management tools, performance monitoring tools, and resource tagging.
Optimizing Resource Utilization
In cloud computing, optimizing resource utilization involves maximizing the efficiency and performance of cloud resources while minimizing costs. This section explores strategies and techniques for achieving optimal resource utilization in cloud environments.
There are several strategies for optimizing resource utilization in cloud computing environments:
- Rightsizing: Rightsizing involves selecting the appropriate size and type of cloud resources (e.g., CPU, memory, storage) to match the actual workload requirements. By avoiding over-provisioning or under-provisioning resources, organizations can optimize costs and improve performance.
- Load Balancing: Load balancing distributes incoming traffic or workload across multiple cloud resources, such as servers or virtual machines, to ensure optimal resource utilization and prevent bottlenecks. Load balancers can be configured to automatically adjust resource allocation based on demand, improving application performance and scalability.
- Auto-scaling: Auto-scaling allows cloud resources to scale up or down automatically based on changing demand. This helps ensure that resources are always available to meet demand while avoiding unnecessary costs during periods of low usage. Auto-scaling can be configured to scale resources based on various metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, or network traffic.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Monitoring and analytics play a crucial role in identifying and addressing resource inefficiencies. By continuously monitoring resource utilization, organizations can identify underutilized or overutilized resources and take appropriate actions to optimize resource allocation. Analytics can help identify trends, patterns, and anomalies in resource usage, enabling proactive resource management and capacity planning.
Rightsizing
Rightsizing is the process of selecting the appropriate size and type of cloud resources to match the actual workload requirements. This involves considering factors such as the number of users, the type of applications, and the expected usage patterns. By rightsizing resources, organizations can avoid over-provisioning, which can lead to wasted costs, and under-provisioning, which can result in performance issues.
Load Balancing
Load balancing is a technique used to distribute incoming traffic or workload across multiple cloud resources, such as servers or virtual machines. This helps ensure optimal resource utilization and prevent bottlenecks. Load balancers can be configured to automatically adjust resource allocation based on demand, improving application performance and scalability.
There are various load balancing algorithms, such as round-robin, least connections, and weighted round-robin, which can be chosen based on the specific requirements of the application.
Auto-scaling
Auto-scaling is a feature provided by many cloud platforms that allows cloud resources to scale up or down automatically based on changing demand. This helps ensure that resources are always available to meet demand while avoiding unnecessary costs during periods of low usage.
Auto-scaling can be configured to scale resources based on various metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, or network traffic. By using auto-scaling, organizations can optimize resource utilization and improve application performance and availability.
Managing Costs
Effectively managing costs is essential for optimizing cloud computing expenses and maximizing the value of cloud resources. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of cost management strategies, pricing models, and techniques to control cloud spending.
Understanding the various pricing models offered by cloud providers is crucial for cost optimization. The pay-as-you-go model, also known as the consumption-based model, charges users based on their actual usage. Reserved instances offer a discounted rate for committing to a specific amount of resources for a specified period, providing significant cost savings for predictable workloads.
Spot instances, on the other hand, allow users to bid on unused capacity at a discounted rate, making them suitable for non-critical workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
Budgeting, forecasting, and tracking cloud usage are essential aspects of cost management. Establishing a clear budget for cloud expenses helps organizations stay within their financial limits. Accurate forecasting of cloud usage patterns enables proactive planning and resource allocation, avoiding overprovisioning or underprovisioning.
Regular tracking of cloud usage provides insights into resource utilization and helps identify opportunities for cost optimization.
Optimizing Resource Utilization
Optimizing resource utilization is a key strategy for reducing cloud costs. Techniques such as rightsizing, autoscaling, and load balancing can help organizations ensure that they are using the appropriate resources for their workloads and avoiding unnecessary expenses. Rightsizing involves selecting the most suitable instance type and size for a specific workload, ensuring that resources are not overprovisioned or underutilized.
Autoscaling allows resources to be automatically scaled up or down based on demand, ensuring that workloads are always running on the optimal amount of resources. Load balancing distributes traffic across multiple instances, improving application performance and preventing resource bottlenecks.
Monitoring and Cost Optimization Tools
Leveraging monitoring and cost optimization tools can significantly enhance cost management efforts. These tools provide real-time visibility into cloud resource usage, costs, and performance metrics. They enable organizations to identify cost anomalies, optimize resource allocation, and make informed decisions to reduce cloud expenses.
Some popular monitoring and cost optimization tools include Amazon CloudWatch, Google Cloud Monitoring, Microsoft Azure Monitor, and third-party solutions such as CloudHealth by VMware and Apptio Cloudability.
Security Considerations
The advent of cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. However, this paradigm shift has also introduced a unique set of security challenges and risks that organizations must address to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data and systems.
The shared responsibility model, where cloud providers and customers share the responsibility for securing cloud-based systems, underscores the importance of collaboration and communication between both parties.
Encryption
Encryption is a cornerstone of cloud security, ensuring that data remains confidential even if intercepted during transmission or storage. Various encryption methods, such as symmetric-key encryption and asymmetric-key encryption, can be employed to protect data at rest and in transit.
Access Control
Access control mechanisms play a vital role in regulating who can access cloud resources and what actions they can perform. Role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) are commonly used to define fine-grained access policies.
Threat Detection and Response
Continuous monitoring and threat detection are crucial for identifying and responding to security incidents promptly. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions can be deployed to detect anomalous activities and provide real-time alerts.
Shared Responsibility Model
The shared responsibility model in cloud computing Artikels the respective responsibilities of cloud providers and customers in securing cloud-based systems. While cloud providers are responsible for securing the underlying infrastructure and platform, customers retain responsibility for securing their data, applications, and configurations.
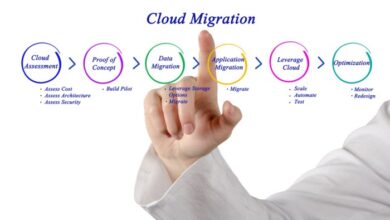
Migration Strategies
Migrating applications and data to the cloud involves careful planning, execution, and monitoring. Different migration strategies exist, each with its own benefits, challenges, and best practices. Understanding these strategies is essential for a successful cloud migration.
Step-by-Step Guide for Cloud Migration
Planning:
- Define migration goals and objectives.
- Assess applications and data for cloud suitability.
- Select a suitable cloud platform and migration strategy.
Execution:
- Prepare the cloud environment.
- Migrate applications and data in a controlled manner.
- Test and validate the migrated systems.
Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor system performance and availability.
- Identify and address any issues or bottlenecks.
- Optimize resource utilization and costs.
Challenges and Best Practices
Lift-and-Shift:
- Challenges: Limited scalability, potential performance issues, security risks.
- Best Practices: Assess application suitability, optimize cloud infrastructure, implement security measures.
Re-platforming:
- Challenges: Requires application modifications, potential downtime, integration issues.
- Best Practices: Choose compatible cloud services, plan for refactoring, test thoroughly.
Re-architecting:
- Challenges: Significant development effort, potential disruption, cost implications.
- Best Practices: Identify suitable cloud-native architectures, plan for phased migration, engage skilled developers.
Future Trends
The realm of cloud computing is undergoing a constant evolution, driven by advancements in technology and the ever-changing demands of businesses. These trends shape the future of cloud resource management and offer new opportunities for businesses to optimize their IT infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming the way cloud resources are managed. AI-powered tools analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict trends, and automate resource allocation. ML algorithms optimize resource utilization by continuously learning from historical usage data and adjusting resource allocation accordingly.
This leads to improved performance, cost savings, and better overall efficiency.
Edge Computing
Edge computing brings cloud computing capabilities closer to the edge of the network, such as IoT devices and remote branch offices. This reduces latency, improves responsiveness, and enhances security. Edge computing enables real-time data processing and decision-making, making it ideal for applications like autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and industrial IoT.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a cloud computing model where the cloud provider manages the underlying infrastructure, including servers, operating systems, and middleware. Developers can focus on writing code without worrying about managing servers. Serverless computing eliminates the need for capacity planning and server maintenance, simplifying application development and reducing costs.
Last Point
The journey to finding the right cloud computing resources is a transformative one, enabling businesses to unlock new possibilities and drive innovation. By understanding your business requirements, evaluating cloud providers, and optimizing resource utilization, you can harness the power of the cloud to achieve operational excellence.
Embrace the cloud’s transformative potential and embark on a path of digital transformation that will propel your business to new heights of success.