Optimizing Cloud Applications for Peak Performance: A Comprehensive Guide
Architecture and Design
In the realm of cloud applications, selecting the appropriate cloud architecture serves as the cornerstone for optimal application performance. By carefully considering the application’s specific requirements, such as scalability, latency, and availability, organizations can optimize their cloud architecture to enhance performance and ensure a seamless user experience.
To optimize the application’s architecture for scalability and efficiency, several strategies can be employed:
- Modular Design: Deconstruct the application into independent modules or microservices, allowing for individual scaling and deployment.
- Load Balancing: Implement load balancers to distribute traffic evenly across multiple servers or instances, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring high availability.
- Caching: Utilize caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed data in memory, reducing the need for repeated database queries and improving response times.
- Asynchronous Processing: Employ asynchronous processing techniques to handle long-running tasks or processes in the background, preventing them from blocking the main application thread.
Furthermore, leveraging cloud-native design patterns and services can significantly improve application performance. These patterns and services are specifically tailored for cloud environments and offer various benefits, including:
- Serverless Computing: Utilize serverless computing platforms to eliminate the need for managing and scaling servers, allowing developers to focus on application logic and functionality.
- Containerization: Employ containerization technologies, such as Docker and Kubernetes, to package and deploy applications in isolated and portable containers, enhancing agility and scalability.
- Cloud-Native Databases: Opt for cloud-native databases, such as NoSQL databases or managed SQL services, which are designed for scalability, high availability, and ease of management.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Implement CDNs to distribute static content, such as images and videos, across multiple edge locations, reducing latency and improving content delivery speed.
Resource Allocation and Management
In the dynamic realm of cloud computing, efficient resource allocation is paramount to ensure optimal performance and cost-effectiveness for cloud applications. By judiciously allocating resources, you can avoid resource wastage, minimize costs, and enhance application responsiveness.
Optimizing resource utilization is a multi-faceted endeavor, encompassing strategies like auto-scaling, load balancing, and proactive monitoring.
Auto-scaling
Auto-scaling is a dynamic resource allocation technique that automatically adjusts resource allocation based on application demand. When demand surges, auto-scaling seamlessly scales up resources to accommodate the increased load. Conversely, when demand subsides, it scales down resources to optimize resource utilization and reduce costs.
- Reactive Scaling: Responds to changes in demand after they occur.
- Predictive Scaling: Leverages historical data and machine learning algorithms to anticipate demand patterns and proactively adjust resources.
Load Balancing
Load balancing distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers or instances to optimize resource utilization and improve application responsiveness. By distributing the load, load balancing prevents overloading individual resources and ensures consistent performance.
- Round Robin: Distributes requests sequentially to servers.
- Least Connections: Directs requests to the server with the fewest active connections.
- Weighted Round Robin: Assigns different weights to servers based on their capacity, ensuring requests are routed to servers with higher capacity.
Monitoring and Analysis
Continuously monitoring and analyzing resource usage patterns is crucial for identifying potential bottlenecks and optimizing resource allocation. By tracking metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, and network traffic, you can gain insights into application behavior and resource consumption patterns.
Leveraging monitoring tools and analytics platforms, you can detect anomalies, identify trends, and proactively address resource-related issues before they impact application performance.
Data Management and Storage

The selection of appropriate data storage options and effective data management strategies significantly impact the performance and efficiency of cloud applications. Let’s delve into these aspects to understand how they influence application performance and explore recommendations for optimizing data storage and access.
Data Storage Options and Their Impact on Performance
Choosing the right data storage option is crucial for optimizing application performance. Different storage types, such as relational databases, NoSQL databases, and object storage, have distinct characteristics that suit specific application requirements.
- Relational Databases:
- NoSQL Databases:
- Object Storage:
Relational databases, like MySQL or PostgreSQL, are well-suited for structured data that requires complex queries and ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) transactions. However, they may not be ideal for applications that require high scalability or real-time data processing.
NoSQL databases, like MongoDB or Cassandra, offer high scalability and flexibility, making them suitable for applications that handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data. They are often used for real-time data processing and applications that require horizontal scaling.
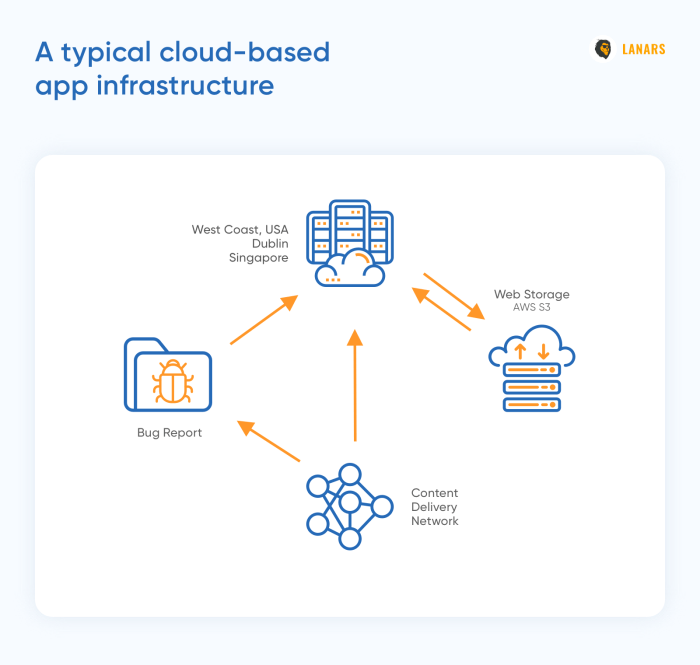
Object storage, like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage, is a cost-effective option for storing large amounts of unstructured data, such as media files, backups, and archives. It provides simple APIs for storing and retrieving objects and is often used in conjunction with other data storage options.
Selecting the Most Suitable Data Storage Option
To select the most suitable data storage option, consider the following factors:
- Data Structure:
- Data Access Patterns:
- Performance Requirements:
Assess the structure and complexity of your data. Relational databases excel at managing structured data with defined relationships, while NoSQL databases are more suitable for unstructured or semi-structured data.
Analyze how your application accesses and updates data. If your application requires complex queries and ACID transactions, a relational database may be a better choice. For applications that require high scalability and real-time data processing, a NoSQL database might be more appropriate.
Consider the performance requirements of your application, including latency, throughput, and scalability. Different data storage options offer varying levels of performance characteristics, so choose the one that best meets your application’s needs.
Optimizing Data Access and Retrieval
To minimize latency and improve application responsiveness, consider the following strategies for optimizing data access and retrieval:
- Data Partitioning:
- Caching:
- Indexing:
- Query Optimization:
Partitioning large datasets across multiple servers or storage nodes can improve performance by distributing the load and reducing the time it takes to access data.
Caching frequently accessed data in memory can significantly reduce latency. Implement caching mechanisms to store frequently used data in memory for faster retrieval.
Creating indexes on frequently queried fields can accelerate data retrieval by allowing the database to quickly locate the desired data without having to scan the entire dataset.
Optimize your queries to improve their efficiency. Use appropriate indexes, avoid unnecessary joins, and optimize the order of operations in your queries.
Network Optimization
Optimizing network performance is crucial for cloud applications, as latency and bandwidth directly impact user experience and application responsiveness. Network latency, the time taken for data to travel between two points, can be reduced by minimizing the physical distance between the application and the user.
This can be achieved by selecting cloud regions closer to the majority of users and employing fast and reliable network connections. Additionally, reducing the number of network hops and optimizing routing can further decrease latency.
Bandwidth Optimization
Adequate bandwidth is essential for handling large data transfers and maintaining application performance. Provisioning sufficient bandwidth ensures that data can flow smoothly without causing bottlenecks or congestion. Techniques like traffic shaping and load balancing can be used to distribute network traffic evenly across available resources, preventing oversubscription and optimizing bandwidth utilization.
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Content delivery networks (CDNs) are distributed networks of servers that store cached copies of static content, such as images, videos, and scripts, closer to end-users. By delivering content from a server located near the user, CDNs significantly reduce latency and improve content delivery speed.
This is particularly beneficial for applications that serve a global audience or experience high volumes of traffic.
Load Balancers
Load balancers are devices or software that distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers or resources. By directing traffic to the most appropriate server based on factors like load, availability, and performance, load balancers help improve application scalability, reliability, and responsiveness.
Load balancers also play a crucial role in failover scenarios, ensuring that traffic is seamlessly redirected to available resources in case of server failure or maintenance.
Caching and Content Delivery

By implementing caching mechanisms, applications can store frequently accessed data in temporary storage for faster retrieval, reducing server load and improving response times.
Choosing Appropriate Caching Strategies
Choosing the appropriate caching strategy depends on various factors such as application requirements, data characteristics, and traffic patterns. Some common caching strategies include:
- In-memory Caching: Stores data in the application’s memory for ultra-fast access. Ideal for frequently accessed, small-sized data.
- Distributed Caching: Distributes cached data across multiple servers or nodes to handle high traffic volumes and improve scalability.
Optimizing Content Delivery
Optimizing content delivery involves leveraging technologies like Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and reverse proxies to reduce latency and improve user experience.
- CDN: A CDN distributes content from multiple geographically dispersed servers, ensuring fast delivery to users regardless of their location.
- Reverse Proxy: Acts as an intermediary between clients and servers, caching static content and load balancing requests to improve performance and scalability.
Monitoring and Performance Tuning
In the realm of cloud applications, monitoring and performance tuning are crucial practices that ensure optimal performance and availability. By proactively monitoring application metrics and employing performance profiling tools, you gain invaluable insights into the behavior and bottlenecks of your cloud-based systems.
Selecting Appropriate Monitoring Tools and Techniques
Choosing the right monitoring tools and techniques is essential for effective performance management. Consider the following factors when making your selection:
- Scalability: Ensure the tool can handle the volume and complexity of your cloud environment.
- Real-time Monitoring: Opt for tools that provide real-time visibility into application performance metrics.
- Customizable Alerts: Choose tools that allow you to set customized alerts and notifications for specific performance thresholds.
- Integration Capabilities: Consider tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing cloud infrastructure and development tools.
Utilizing Performance Profiling Tools
Performance profiling tools are invaluable for identifying and addressing performance bottlenecks in your cloud applications. These tools provide detailed insights into the runtime behavior of your applications, helping you pinpoint areas that require optimization.
- Profiling Techniques: Utilize techniques such as sampling, instrumentation, and tracing to collect performance data.
- Bottleneck Identification: Analyze profiling data to identify bottlenecks, such as slow database queries, inefficient algorithms, or network latency issues.
- Code Optimization: Use profiling results to optimize your code, eliminate inefficiencies, and improve overall performance.
Security and Compliance
Security measures are crucial for protecting cloud applications from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other malicious activities. However, implementing security measures can potentially impact application performance, especially if not done efficiently. Striking a balance between security and performance is essential for ensuring optimal application performance while maintaining a robust security posture.
Implementing Security Measures with Minimal Performance Overhead
Employ lightweight security mechanisms
Use security solutions that have a minimal impact on application performance. For example, consider using a web application firewall (WAF) that is designed for high-performance environments or implementing security features natively within the application code to avoid additional layers of security infrastructure.
Implement security measures at the appropriate level
Avoid applying security measures across the entire application indiscriminately. Instead, focus on securing only the critical and sensitive parts of the application. This targeted approach helps minimize the performance impact while still ensuring adequate security.
Leverage cloud security services
Cloud platforms offer a range of built-in security services that can be easily integrated with cloud applications. These services are designed to provide robust security without compromising performance, as they are optimized for the cloud environment.
Complying with Regulatory and Industry-Specific Security Standards
Understand the requirements
Familiarize yourself with the specific security standards and regulations that apply to your industry or region. This will help you tailor your security measures accordingly and avoid implementing unnecessary or redundant security controls that could affect performance.
Use compliant cloud platforms
Choose a cloud platform that offers built-in compliance features and certifications. This can significantly reduce the effort and resources required to comply with regulatory standards, allowing you to focus on optimizing application performance.
Implement security best practices
Adhere to industry-standard security best practices, such as regular security audits, vulnerability management, and incident response planning. These practices help maintain a secure application environment without compromising performance.
Final Thoughts
Optimizing cloud application performance is a continuous journey, requiring ongoing monitoring, analysis, and fine-tuning. By adopting a proactive approach, organizations can stay ahead of potential bottlenecks, ensure seamless application operation, and deliver exceptional user experiences. With the strategies Artikeld in this guide, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of cloud computing, unlocking the true power of their cloud applications and driving organizational growth.