Navigating the Cloud: A Comprehensive Guide to Cloud Migration
Pre-Migration Considerations
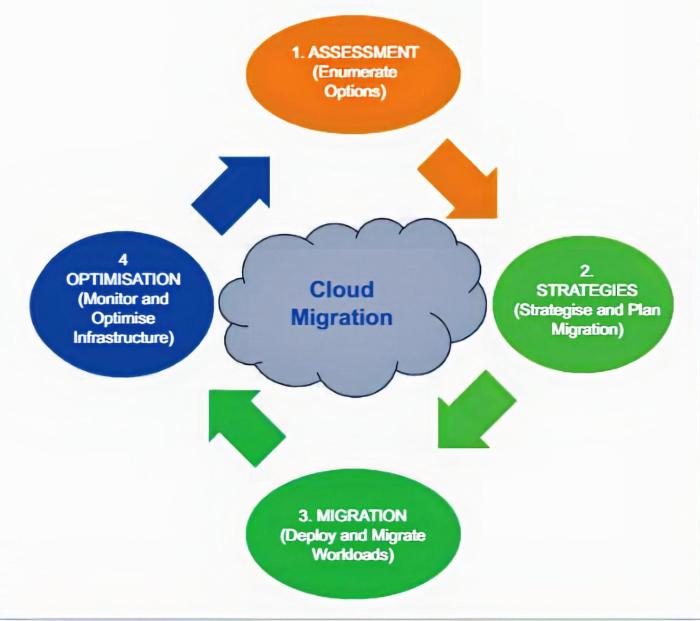
Effective cloud migration necessitates careful planning and preparation. Before embarking on the migration process, it is crucial to define clear migration goals and objectives. This involves understanding the specific outcomes you aim to achieve, such as cost optimization, improved agility, or enhanced security.
To ensure a successful migration, it is essential to assess your current IT infrastructure and applications for cloud readiness. This involves evaluating factors such as compatibility with cloud platforms, dependencies, and performance requirements. It is also important to consider the impact of migration on users and stakeholders, as well as the overall cost and timeline of the migration process.
Checklist of Factors to Consider Before Migrating to the Cloud
- Clearly defined migration goals and objectives.
- Assessment of current IT infrastructure and applications for cloud readiness.
- Identification of dependencies and potential migration risks.
- Evaluation of cloud platforms and services that align with your specific requirements.
- Consideration of the impact of migration on users and stakeholders.
- Development of a comprehensive migration plan and timeline.
- Allocation of adequate resources and budget for the migration process.
Choosing the Right Cloud Migration Strategy
Migrating to the cloud is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Choosing the right migration strategy is critical to ensuring a successful migration. There are three main cloud migration strategies: lift and shift, re-platforming, and re-architecting.
Lift and Shift
Lift and shift is the simplest and least expensive migration strategy. In this approach, applications and data are moved to the cloud with minimal changes. This strategy is best suited for applications that are not heavily reliant on the underlying infrastructure and can be easily moved to the cloud without significant modifications.
Pros:
- Simple and inexpensive
- Minimal disruption to business operations
- Quick and easy to implement
Cons:
- May not take advantage of all the benefits of the cloud
- Can lead to higher costs in the long run
- May not be suitable for applications that are heavily reliant on the underlying infrastructure
Re-platforming
Re-platforming involves migrating applications to a different platform in the cloud. This strategy is best suited for applications that are not compatible with the current cloud platform or that can benefit from the features and capabilities of a different platform.
Pros:
- Can take advantage of the features and capabilities of a different cloud platform
- Can improve performance and scalability
- Can reduce costs in the long run
Cons:
- More complex and expensive than lift and shift
- Can be disruptive to business operations
- Requires more time to implement
Re-architecting
Re-architecting involves redesigning and rebuilding applications to take advantage of the cloud’s unique features and capabilities. This strategy is best suited for applications that are heavily reliant on the underlying infrastructure or that need to be significantly modified to run in the cloud.
Pros:
- Can take full advantage of the cloud’s benefits
- Can improve performance and scalability
- Can reduce costs in the long run
Cons:
- Most complex and expensive migration strategy
- Most disruptive to business operations
- Requires the most time to implement
Selecting the Right Migration Strategy
The best cloud migration strategy for a particular organization will depend on a number of factors, including the organization’s budget, timeline, risk tolerance, and the applications that are being migrated.
- Organizations with a limited budget and timeline may opt for a lift and shift migration.
- Organizations that need to take advantage of the features and capabilities of a different cloud platform may opt for a re-platforming migration.
- Organizations that need to significantly modify their applications to run in the cloud may opt for a re-architecting migration.
It is important to carefully consider all of the factors involved before selecting a cloud migration strategy. By choosing the right strategy, organizations can ensure a successful migration that meets their business needs.
Planning and Preparing for Migration
Thorough planning and preparation are crucial for a successful cloud migration. This involves creating a detailed migration plan, conducting risk assessments, and establishing a communication plan.
Migration Plan
A comprehensive migration plan Artikels the steps, timeline, and resources required for a smooth transition to the cloud. It should include:
- Assessment of current IT infrastructure and applications
- Selection of the appropriate cloud platform and migration strategy
- Detailed migration steps, including data transfer, application reconfiguration, and testing
- Timeline with milestones and deadlines
- Resource allocation, including personnel, budget, and tools
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
Cloud migration involves inherent risks that need to be identified and addressed. Common risks include data security, downtime, compatibility issues, and cost overruns. To mitigate these risks, consider the following best practices:
- Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and risks.
- Develop a risk mitigation plan that Artikels strategies to address each identified risk.
- Implement security measures to protect data and applications during migration.
- Create a backup and recovery plan to ensure data integrity and minimize downtime.
- Monitor the migration process closely and make adjustments as needed.
Communication Plan
A well-defined communication plan ensures that all stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the migration process. This plan should include:
- Identification of key stakeholders, including IT personnel, business leaders, and end-users
- Regular communication channels, such as email updates, meetings, and webinars
- Clear and concise messaging that explains the migration process, benefits, and potential impacts
- A feedback mechanism to address stakeholder concerns and questions
Data Migration Techniques
Migrating data to the cloud involves various techniques that enable seamless transfer and integration with cloud-based systems. These techniques address the specific requirements of different data types, volumes, and migration scenarios.
Factors to consider when selecting the appropriate data migration technique include:
- Data volume and size: Assess the amount of data to be migrated and its impact on network bandwidth and migration duration.
- Data type and sensitivity: Consider the nature of the data, its sensitivity, and any regulatory or compliance requirements.
- Source and target systems: Evaluate the compatibility between the source and target systems, including operating systems, databases, and applications.
- Migration budget and timeline: Determine the available resources and time constraints for the migration process.
Data Replication
Data replication involves copying data from the source system to the cloud in real time or at regular intervals. This technique ensures that the data remains consistent across both systems, providing high availability and disaster recovery capabilities.
Data Synchronization
Data synchronization is similar to data replication, but it involves periodically synchronizing data between the source and cloud systems. This technique is suitable for scenarios where real-time data replication is not required or where data volumes are large.
Bulk Data Transfer
Bulk data transfer involves transferring large volumes of data from the source system to the cloud in a single operation. This technique is commonly used for initial data migration or when migrating large datasets that do not require real-time synchronization.
Tips for Ensuring Data Integrity and Security During Migration
- Plan and test thoroughly: Develop a comprehensive migration plan that addresses data integrity and security requirements. Conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve potential issues before the actual migration.
- Use secure data transfer methods: Employ encryption and secure protocols to protect data during transfer. Utilize reputable cloud service providers that offer robust security measures.
- Monitor and manage data access: Implement strict access controls and monitoring mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access to data during and after migration.
- Create and test data recovery plans: Develop and test data recovery plans to ensure that data can be restored quickly and efficiently in case of any issues or disasters.
Application Migration Considerations
Migrating applications to the cloud presents both challenges and opportunities. Understanding these challenges and following best practices can ensure a smooth and successful migration.
Challenges of Application Migration
- Technical Complexity: Applications can be complex, involving multiple components, dependencies, and integrations. Migrating these applications to the cloud requires careful planning and technical expertise.
- Cost and Performance: Cloud migration can involve upfront costs and ongoing expenses. It’s crucial to assess the cost-benefit ratio and ensure that the cloud environment meets the application’s performance requirements.
- Security and Compliance: Migrating applications to the cloud raises security and compliance concerns. Organizations need to ensure that the cloud provider’s security measures align with their regulatory and industry standards.
- Data Residency and Sovereignty: Organizations must consider data residency and sovereignty requirements when migrating applications to the cloud. Some regulations may restrict where data can be stored or processed.
Best Practices for Application Migration
- Refactoring and Optimization: Refactoring applications to optimize their performance and efficiency in the cloud environment is crucial. This includes modernizing the application architecture, removing unnecessary code, and optimizing resource utilization.
- Phased Migration: Migrating applications in phases can reduce risks and minimize disruption. Organizations can start with non-critical applications and gradually migrate more complex applications as they gain experience and confidence.
- Leveraging Cloud-Native Services: Cloud providers offer a wide range of services that can enhance application performance and scalability. Organizations should leverage these services to optimize their applications for the cloud environment.
- Managing Application Dependencies: Identifying and managing application dependencies is critical to ensure that the application functions correctly in the cloud. This includes managing dependencies on other applications, libraries, and services.
- Ensuring Compatibility with Cloud Services: Organizations need to ensure that their applications are compatible with the cloud services they plan to use. This includes testing the application with the cloud provider’s APIs and ensuring that the application can integrate seamlessly with other cloud services.
Managing Application Dependencies
Managing application dependencies is crucial for a successful cloud migration. Organizations should:
- Identify and Document Dependencies: Identify all the dependencies of the application, including libraries, frameworks, and services. Document these dependencies and their versions.
- Assess Compatibility: Evaluate the compatibility of the dependencies with the cloud environment. Ensure that the dependencies are supported in the cloud and that they are compatible with the cloud provider’s services.
- Update or Replace Dependencies: If necessary, update or replace dependencies to ensure compatibility with the cloud environment. This may involve upgrading to newer versions or migrating to cloud-compatible alternatives.
- Test and Monitor Dependencies: Test the application with the updated or replaced dependencies to ensure that it functions correctly. Continuously monitor the dependencies to detect any issues or vulnerabilities.
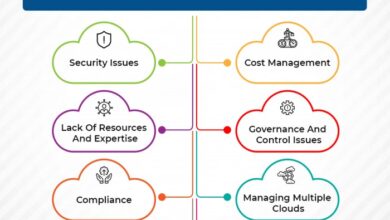
Security and Compliance in Cloud Migration
Ensuring security and maintaining compliance during cloud migration is crucial. Understanding the shared responsibility model and implementing robust security measures is essential for protecting data and adhering to regulations.
Shared Responsibility Model for Security
In cloud environments, the shared responsibility model defines the security responsibilities between the cloud provider and the customer. The cloud provider is responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure, while the customer is responsible for the security of their data, applications, and workloads.
Security Measures during Cloud Migration
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implement role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to control user access to cloud resources.
- Network Security: Configure firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to protect against network attacks.
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly scan cloud resources for vulnerabilities and patch them promptly.
- Security Monitoring: Implement security monitoring tools to detect and respond to security incidents in real time.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop an incident response plan that Artikels the steps to be taken in case of a security incident.
Compliance Requirements and Best Practices
Organizations migrating to the cloud must comply with various regulations and industry standards. Some common compliance requirements include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): GDPR applies to organizations that process personal data of individuals in the European Union.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA applies to organizations that handle protected health information (PHI) in the United States.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS): PCI DSS applies to organizations that process payment card data.
Best practices for maintaining compliance in the cloud include:
- Choose a compliant cloud provider: Select a cloud provider that offers compliance certifications and has a track record of meeting regulatory requirements.
- Implement compliance controls: Implement technical and organizational measures to meet compliance requirements.
- Regularly audit compliance: Conduct regular audits to ensure that compliance requirements are being met.
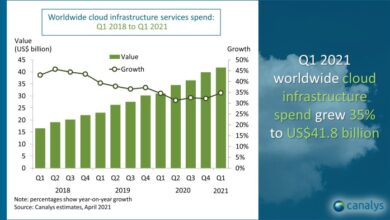
Cost Optimization Strategies
Cost optimization is a crucial aspect of cloud migration, as it helps organizations avoid unnecessary expenses and maximize the value of their cloud investment. Several factors influence cloud migration costs, including the size and complexity of the migrated workload, the chosen cloud provider and services, and the migration strategy adopted.
To optimize cloud costs, organizations can implement various strategies, including:
Resource Utilization Monitoring
- Continuously monitor cloud resource utilization to identify underutilized or idle resources. This helps organizations right-size their cloud infrastructure and eliminate unnecessary costs.
- Utilize cloud-native tools and services that provide detailed insights into resource usage, such as Amazon CloudWatch or Google Cloud Monitoring.
Cost-Effective Cloud Services
- Select cloud services that align with the specific needs and requirements of the migrated workload. Avoid using premium or higher-priced services unless necessary.
- Explore cost-saving options offered by cloud providers, such as spot instances, reserved instances, or committed use discounts.
Optimizing Application Architecture
- Design and architect applications to be cloud-native, taking advantage of cloud-specific features and services to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Implement serverless architectures or microservices to minimize resource consumption and optimize scalability.
Cloud Cost Management Tools
- Utilize cloud cost management tools and services provided by cloud providers or third-party vendors. These tools offer comprehensive insights into cloud spending, enabling organizations to track costs, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
- Set up budget alerts and notifications to stay informed about potential cost overruns and take corrective actions promptly.
Post-Migration Monitoring and Management
Post-migration monitoring and management are crucial for ensuring the ongoing health and performance of cloud infrastructure and applications. Continuous monitoring allows organizations to detect and address issues promptly, optimize resource utilization, and ensure compliance with security and regulatory requirements.
Setting up effective monitoring tools and metrics is essential for successful cloud management. These tools should provide real-time visibility into system performance, resource usage, and security events. Metrics should be carefully selected to align with specific business objectives and KPIs, allowing organizations to track key performance indicators and identify areas for improvement.
Incident Response and Disaster Recovery
Organizations should establish clear incident response and disaster recovery plans to ensure rapid and effective response to unexpected events. These plans should include well-defined roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and procedures for identifying, isolating, and resolving incidents. Regular testing and drills are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of these plans.
Outcome Summary
As you embark on your cloud migration journey, remember that preparation, planning, and continuous monitoring are key to a successful transition. By carefully assessing your needs, choosing the right migration strategy, and implementing robust security measures, you can unlock the full potential of the cloud.
Embrace the cloud’s transformative power and watch your business soar to new heights of innovation and growth.