Cloud Computing’s Evolving Landscape: Unveiling the Latest Trends and Innovations
Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud Strategies
The proliferation of cloud services and applications has led organizations to adopt hybrid and multi-cloud strategies to optimize their IT infrastructure and improve agility.
Hybrid cloud combines on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, providing flexibility and control over sensitive data and applications while leveraging the scalability and cost-effectiveness of the cloud. Multi-cloud involves using multiple public cloud providers to distribute workloads and services, enhancing redundancy, availability, and vendor lock-in avoidance.
Benefits of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Approaches
- Cost Optimization: Organizations can allocate workloads to the most cost-effective environment, reducing overall IT expenses.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Hybrid and multi-cloud environments enable organizations to scale resources up or down quickly to meet changing demands.
- Improved Performance and Reliability: By distributing workloads across multiple clouds, organizations can improve application performance and reliability, minimizing downtime.
- Data Sovereignty and Compliance: Hybrid cloud allows organizations to retain sensitive data on-premises while leveraging cloud services for non-critical workloads, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Challenges of Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Approaches
- Complexity and Management Overhead: Managing multiple clouds and ensuring interoperability can be complex and time-consuming.
- Security and Compliance: Organizations must address security and compliance requirements across multiple cloud environments, which can be challenging.
- Data Integration and Governance: Integrating data and maintaining consistent data governance policies across hybrid and multi-cloud environments can be complex.
Role of Containerization and Orchestration Tools
Containerization and orchestration tools, such as Docker and Kubernetes, play a crucial role in enabling hybrid and multi-cloud environments. These tools allow organizations to package applications and their dependencies into portable containers that can be deployed and managed consistently across different cloud platforms.
Containerization and orchestration tools simplify the deployment and management of applications in hybrid and multi-cloud environments, improving portability, scalability, and agility.
Edge Computing and Distributed Cloud
Edge computing is a distributed computing paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the devices and locations where it is needed, enabling faster and more efficient processing.
Edge computing complements cloud computing by extending the cloud to the edge of the network, enabling real-time data processing, improved responsiveness, and reduced latency. It is particularly useful for applications that require low latency, high bandwidth, and real-time processing, such as self-driving cars, industrial automation, and remote healthcare.
Benefits of Edge Computing
- Reduced latency: Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, minimizing the distance data must travel, resulting in faster response times and improved user experience.
- Improved bandwidth utilization: Edge computing reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud, freeing up bandwidth for other applications.
- Increased reliability: Edge computing can improve the reliability of applications by providing local data storage and processing, making them less susceptible to network outages or disruptions.
- Enhanced security: Edge computing can improve security by reducing the amount of data that is transmitted to the cloud, making it less vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Challenges of Edge Computing
- Complexity: Edge computing can be complex to implement and manage, requiring specialized hardware, software, and skills.
- Security: Edge devices can be more vulnerable to security threats due to their distributed nature and limited resources.
- Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between different edge devices and platforms can be challenging.
- Cost: Implementing and maintaining an edge computing infrastructure can be expensive.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
- Self-driving cars: Edge computing enables real-time processing of sensor data, allowing self-driving cars to make quick decisions and respond to changing conditions.
- Industrial automation: Edge computing can be used to monitor and control industrial processes in real time, enabling faster and more efficient operations.
- Remote healthcare: Edge computing can be used to provide real-time monitoring of patients’ vital signs and medical data, enabling remote diagnosis and treatment.
- Smart cities: Edge computing can be used to collect and analyze data from sensors in smart cities, enabling real-time monitoring of traffic, energy consumption, and other urban services.
Serverless Computing
Serverless computing, also known as function-as-a-service (FaaS), is a cloud computing model in which the cloud provider dynamically manages the allocation and provisioning of server resources on demand. It allows developers to build and deploy applications without having to worry about managing the underlying infrastructure, such as servers, operating systems, or middleware.
Serverless computing offers several advantages over traditional server-based architectures, including:
- Cost-effectiveness: Developers only pay for the resources they use, eliminating the need to overprovision or maintain idle servers.
- Scalability: Serverless platforms automatically scale resources up or down based on demand, ensuring optimal performance.
- Simplicity: Developers can focus on writing code and building applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- Reliability: Cloud providers manage the infrastructure, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance.
Popular Serverless Platforms
There are several popular serverless platforms available, each with its own unique features and benefits. Some of the most widely used platforms include:
- AWS Lambda: AWS Lambda is a serverless computing platform offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It allows developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers.
- Google Cloud Functions: Google Cloud Functions is a serverless computing platform offered by Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It allows developers to build and deploy applications that respond to events without managing infrastructure.
- Azure Functions: Azure Functions is a serverless computing platform offered by Microsoft Azure. It allows developers to create and run code without managing servers or infrastructure.
Challenges and Considerations
While serverless computing offers several benefits, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind before adopting it:
- Vendor lock-in: Serverless platforms are often proprietary, which can make it difficult to switch between providers.
- Cold starts: When a serverless function is invoked for the first time, it may take longer to execute due to the cold start process, which involves initializing the function’s runtime environment.
- Limited control: Developers have less control over the underlying infrastructure, which may not be suitable for applications with specific requirements.
- Cost management: It’s important to carefully monitor resource usage to avoid unexpected costs, especially for applications that experience unpredictable traffic patterns.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in the Cloud
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) have become integral parts of cloud computing, enabling businesses to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and gain valuable insights from data. The integration of AI and ML with cloud services offers numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced customer experiences.
Integration of AI and ML with Cloud Computing Services
Cloud providers offer a wide range of AI and ML services that allow developers to easily incorporate these technologies into their applications. These services include pre-built models for common tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics.
Developers can also train their own models using cloud-based tools and resources, enabling them to create custom AI solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Examples of AI and ML in Cloud-Based Applications
AI and ML are being used in a variety of cloud-based applications across different industries. Some notable examples include:
Retail
AI-powered recommendation engines analyze customer behavior and preferences to provide personalized shopping experiences and product recommendations.
Healthcare
ML algorithms are used to analyze medical data and images to aid in diagnosis, treatment planning, and drug discovery.
Finance
AI and ML are employed for fraud detection, credit scoring, and personalized financial advice.
Manufacturing
AI-driven predictive maintenance systems monitor equipment and identify potential issues before they occur, preventing downtime and increasing productivity.
Ethical and Societal Implications of AI and ML in the Cloud
The rapid advancement of AI and ML raises ethical and societal concerns that need to be carefully considered. These include issues related to data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential impact of AI on employment and the workforce. It is essential to address these concerns and develop guidelines and regulations to ensure that AI and ML are used responsibly and ethically.
Cloud Security and Compliance
Cloud computing brings about unique security and compliance challenges due to its shared responsibility model, where the cloud provider and the customer share the responsibility for securing the cloud environment. Common security threats and vulnerabilities in cloud environments include unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, denial-of-service attacks, and insecure configurations.
Best Practices for Cloud Security
Implementing robust security measures is essential for protecting cloud-based applications and data. Some key best practices and recommendations include:
- Shared Responsibility Model: Understand and adhere to the shared responsibility model, clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of both the cloud provider and the customer.
- Encryption: Implement encryption at rest and in transit to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Use role-based access control (RBAC) to grant users only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks.
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly scan and patch cloud systems and applications for vulnerabilities and security updates.
- Incident Response Plan: Establish a comprehensive incident response plan to quickly detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Ensure compliance with relevant industry standards, regulations, and laws, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Cloud Cost Optimization

In the realm of cloud computing, cost optimization stands as a pivotal practice that directly impacts business profitability. By effectively managing and optimizing cloud expenses, organizations can enhance their financial performance and allocate resources more efficiently.
There are several strategies and techniques that can be employed to optimize cloud costs. These include:
- Rightsizing Resources: Continuously monitoring and adjusting cloud resources to ensure that they align with actual usage patterns. This involves scaling up or down as needed, avoiding overprovisioning, and optimizing instance types and sizes.
- Negotiating Contracts: Engaging in strategic negotiations with cloud providers to secure favorable pricing terms, discounts, and service level agreements (SLAs). This can involve negotiating volume discounts, long-term contracts, and customized pricing models.
- Utilizing Reserved Instances: Taking advantage of reserved instances, which offer significant cost savings in exchange for a commitment to a specific level of usage over a fixed term. This option is ideal for predictable and consistent workloads.
- Leveraging Spot Instances: Employing spot instances, which are unused cloud resources available at deeply discounted rates. These instances can be leveraged for non-critical workloads that can tolerate interruptions.
- Optimizing Cloud Architecture: Designing and implementing cloud architectures that are efficient and cost-effective. This involves optimizing network configurations, utilizing appropriate storage types, and implementing load balancing and auto-scaling mechanisms.
- Implementing Cost Monitoring and Management Tools: Utilizing cloud cost monitoring and management tools to gain visibility into cloud spending, identify cost anomalies, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and optimization.
Additionally, cloud providers offer various tools and services that can assist organizations in monitoring and managing their cloud spending. These tools provide detailed insights into resource usage, cost breakdowns, and trends. By leveraging these tools, organizations can identify areas for cost savings and make proactive adjustments to their cloud infrastructure.
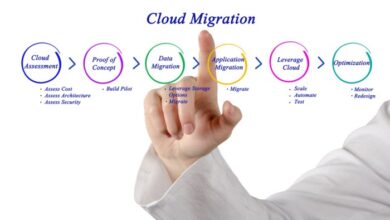
Cloud Migration and Modernization
Cloud migration and modernization involve transitioning existing applications, data, and infrastructure from on-premises or legacy environments to the cloud. This transformation enables organizations to leverage the scalability, agility, and cost-effectiveness of cloud computing.
Effective cloud migration and modernization require careful planning, execution, and ongoing management. Organizations should consider the following key steps and considerations:
Assessment and Planning
- Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the current IT environment, including applications, data, and infrastructure.
- Define clear migration goals and objectives, such as improved performance, cost reduction, or increased agility.
- Develop a detailed migration plan that Artikels the steps, timeline, and resources required for the migration.
Application and Data Migration
- Choose appropriate migration strategies for each application and data set, such as lift-and-shift, re-platforming, or refactoring.
- Ensure that applications are compatible with the target cloud environment and that data is properly transformed and migrated.
- Test and validate the migrated applications and data to ensure they function correctly in the cloud.
Infrastructure and Network Configuration
- Provision and configure the necessary cloud infrastructure, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking.
- Implement appropriate security measures to protect data and applications in the cloud.
- Monitor and manage the cloud infrastructure to ensure optimal performance and availability.
Ongoing Management and Optimization
- Continuously monitor and optimize the cloud environment to ensure it meets performance, cost, and security requirements.
- Regularly review and update cloud migration and modernization strategies to adapt to changing business needs and technological advancements.
- Provide ongoing support and training to IT staff to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge to manage the cloud environment effectively.
Challenges and Risks
Cloud migration and modernization projects can be complex and challenging. Common challenges include:
- Lack of technical expertise and resources to manage the migration.
- Application compatibility issues with the target cloud environment.
- Data security and compliance concerns.
- Cost management and optimization.
- Managing the transition from on-premises to cloud operations.
To mitigate these challenges and risks, organizations should carefully assess their needs, choose the right cloud migration strategy, and work with experienced cloud service providers or consultants.
Best Practices
To ensure successful cloud migration and modernization, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Start with a clear understanding of the business objectives and expected outcomes of the migration.
- Choose the right cloud migration strategy and partner with experienced cloud service providers or consultants.
- Conduct thorough planning and assessment to identify potential challenges and risks.
- Implement a phased migration approach to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition.
- Continuously monitor and optimize the cloud environment to ensure it meets performance, cost, and security requirements.
Cloud Native Development and DevOps
Cloud native development is a modern approach to building and running applications that fully leverage the benefits of cloud computing. It involves adopting a set of principles and practices that enable developers to create applications that are scalable, resilient, and easy to manage in a cloud environment.The
principles of cloud native development include:
Microservices architecture
Building applications as a collection of small, independent services that communicate with each other over a network.
Containerization
Packaging applications and their dependencies into containers that can be easily deployed and managed.
Orchestration
Using a platform to manage and automate the deployment, scaling, and monitoring of containers.
Continuous delivery
Automating the process of building, testing, and deploying applications in a continuous loop.DevOps plays a critical role in cloud native development by enabling teams to adopt and implement these principles and practices. DevOps is a set of practices that emphasize collaboration between development and operations teams to improve the speed and quality of software delivery.DevOps
tools and technologies that support cloud native development include:
Container platforms
Platforms such as Kubernetes and Docker Swarm provide a foundation for deploying and managing containers in a production environment.
Continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) tools
Tools such as Jenkins and CircleCI automate the process of building, testing, and deploying applications.
Monitoring and logging tools
Tools such as Prometheus and ELK Stack help teams monitor the performance and health of their applications.Cloud native development and DevOps enable teams to build and deliver applications that are more scalable, resilient, and easy to manage in a cloud environment.
These approaches help organizations accelerate innovation and deliver value to their customers faster.
Last Word
As we conclude our exploration of the latest trends in cloud computing, it’s evident that this dynamic field is continuously evolving, presenting both challenges and opportunities for businesses and organizations. Embracing these trends can lead to increased efficiency, cost optimization, and innovation.
However, it’s crucial to navigate the complexities of cloud migration and modernization, ensuring a smooth transition while leveraging the benefits of cloud-native development and DevOps practices. The future of cloud computing holds immense promise, and staying abreast of these trends will empower businesses to thrive in the digital age.